Lupus is a fascinating and mysterious condition that captivates the medical world and those affected by it. With its origins rooted in Greek mythology, this autoimmune disease has an enigmatic nature that leaves experts intrigued and researchers determined to unlock its secrets. What does lupus mean for those living with it? It is a chronic illness that disrupts the body’s immune system, causing it to mistakenly attack healthy cells and tissues. This leads to a wide array of symptoms, including extreme fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and even organ damage. The complexity of lupus lies in its unpredictable nature, as symptoms can vary greatly from person to person and flare-ups can occur unexpectedly. Exploring the intricacies of lupus unveils a rich tapestry of medical breakthroughs, ongoing research, and the resilience of individuals living with this condition. It is a field that constantly pushes the boundaries of knowledge and treatment options, offering hope to those seeking relief and a better quality of life. Understanding what lupus means goes beyond the medical realm; it delves into the emotional and psychological impact on individuals and their loved ones. Join us on a journey to unravel the enigma of lupus, as we delve into the latest scientific discoveries, personal stories of triumph, and the relentless pursuit of a cure. Discover the strength and resilience of those living with lupus, and gain insight into the ongoing efforts to improve diagnosis, treatment, and support systems. Together, we can shed light on the mysteries of this complex condition and inspire hope for a brighter future.
What Does Lupus Mean
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Lupus | Lupus, also known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs. |
| Autoimmune Disease | An autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system, which is designed to protect against harmful substances, mistakenly attacks healthy cells, tissues, and organs as if they were foreign invaders. |
| Chronic | Chronic refers to a long-lasting condition that persists over an extended period, typically more than three months. In the case of lupus, it is a lifelong disease with periods of remission and flare-ups. |
| Systemic | Systemic lupus erythematosus affects multiple systems and organs of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, brain, and blood cells. It can cause a wide range of symptoms and complications. |
| Erythematosus | Erythematosus refers to a reddening of the skin, which can be a characteristic feature of lupus, particularly during disease flares or when exposed to sunlight. |
Understanding Lupus: A Comprehensive Guide
Lupus, also known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a complex condition that can manifest in various ways, making it difficult to diagnose and treat. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of lupus, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
The Mysterious Nature of Lupus
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system, which is designed to protect the body from foreign invaders, mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In the case of lupus, the immune system becomes hyperactive and targets various organs and systems, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain. This widespread inflammation can lead to a wide range of symptoms and complications.
Lupus is a highly individualized disease, meaning that its symptoms and severity can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, such as joint pain and fatigue, while others may face more severe manifestations, including organ damage and life-threatening complications.
Unraveling the Causes
The exact cause of lupus remains unknown, but researchers believe that it is likely a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Certain genes have been identified as potential risk factors for developing lupus, but having these genes does not necessarily mean a person will develop the disease. Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals or infections, may trigger lupus in susceptible individuals.
Furthermore, hormones, particularly estrogen, may play a role in the development and progression of lupus. This is evidenced by the fact that lupus predominantly affects women of childbearing age, suggesting a hormonal link. However, the precise mechanisms behind these interactions are yet to be fully understood.
Recognizing the Symptoms
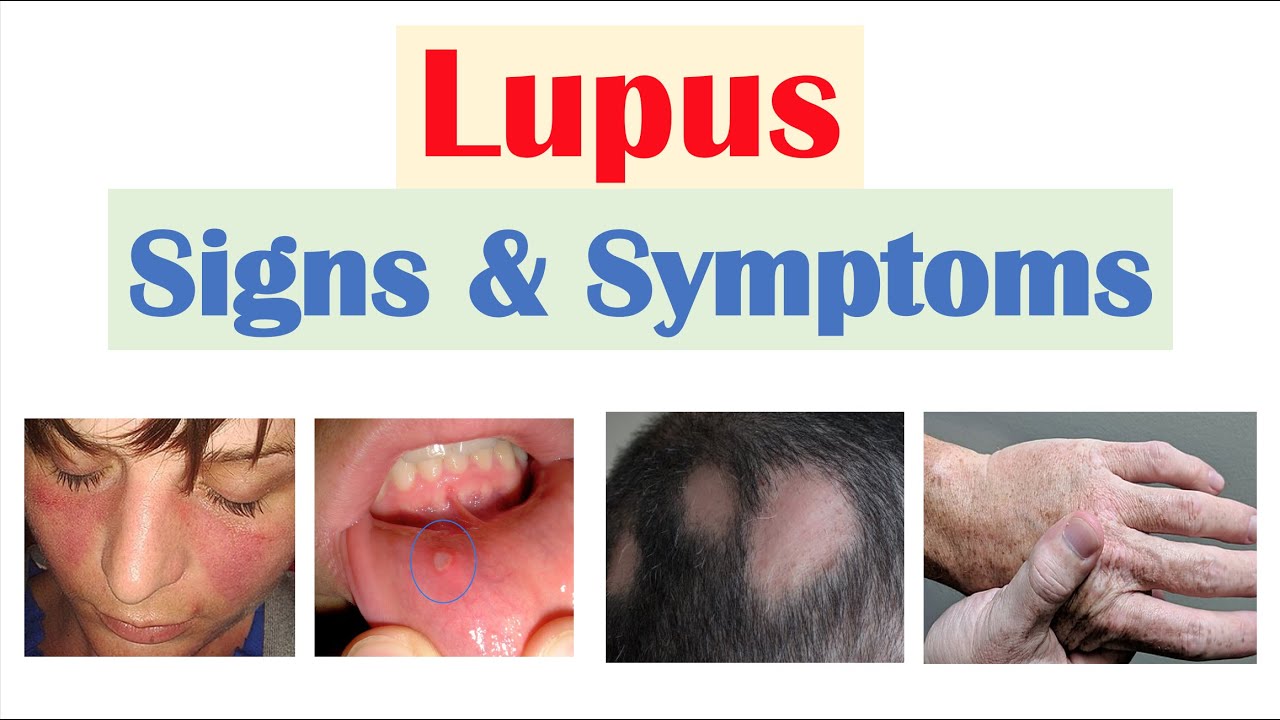
Lupus can present with a wide range of symptoms, which can make it challenging to diagnose. Some of the most common symptoms include extreme fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, fever, hair loss, and photosensitivity (sensitivity to sunlight). However, these symptoms can also be indicative of other conditions, making it crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
In addition to the physical symptoms, many individuals with lupus also experience emotional and mental health challenges. Depression, anxiety, and cognitive difficulties are not uncommon in those living with this chronic illness. Therefore, comprehensive care should address both the physical and emotional aspects of lupus.
Diagnosing Lupus: A Complex Puzzle
Diagnosing lupus can be a complex process, as there is no single test that can definitively confirm its presence. Instead, healthcare professionals rely on a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and the presence of specific criteria outlined by the American College of Rheumatology.
These criteria include symptoms such as facial rash, joint pain, photosensitivity, and abnormal blood test results, among others. If a person meets a certain number of these criteria, a diagnosis of lupus may be made. However, it is important to note that lupus can evolve over time, and additional symptoms may emerge, requiring ongoing monitoring and evaluation.
Managing Lupus: Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for lupus, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and minimize disease activity. The treatment plan for each individual will depend on the severity of their symptoms and the organs affected.
Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and suppress the overactive immune response. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management, can play a significant role in managing lupus.
It is crucial for individuals with lupus to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and concerns. Regular check-ups, ongoing communication, and adherence to prescribed medications are essential for effectively managing this chronic condition.
Conclusion
Lupus is a complex and chronic autoimmune disease that requires a comprehensive understanding and approach for effective management. While it presents unique challenges, advancements in research and treatment options continue to improve the quality of life for individuals living with lupus. By raising awareness and supporting ongoing research efforts, we can strive towards a future where lupus is better understood, diagnosed earlier, and managed more effectively.