Carnivore is not just a simple dietary preference; it’s a thrilling and fascinating concept that unveils the primal essence of the animal kingdom. Exploring the world of carnivores takes you on an extraordinary journey into the realm of predators, where instinct, adaptation, and savage beauty intertwine. Delve into the captivating world of these formidable creatures, and witness their awe-inspiring hunting techniques, their remarkable physical capabilities, and their undeniable place in the delicate balance of nature. Discover how these apex predators, with their razor-sharp teeth and killer instincts, have evolved over millennia to become masters of their domains. Uncover the secrets behind their ferocious hunting strategies, as they stalk their prey with unparalleled precision and speed. From the mighty big cats of the African savannah to the awe-inspiring marine predators lurking beneath the ocean’s surface, the world of carnivores is a thrilling spectacle that will leave you spellbound. Prepare to be captivated by nature’s fiercest and most magnificent creatures, and gain a newfound appreciation for the power, agility, and beauty of these incredible predators.

What is a Carnivore?
| Category | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Obligate Carnivores | Obligate carnivores are animals that rely solely on a diet of meat to meet their nutritional requirements. Their digestive systems are adapted to efficiently process animal tissues. | Lions, tigers, and hyenas |
| Facultative Carnivores | Facultative carnivores are animals that are primarily carnivorous but can also consume plant-based foods to meet their dietary needs, especially during times when prey is scarce. | Domestic cats and several species of bears |
| Hypercarnivores | Hypercarnivores are carnivores that derive a significant proportion of their diet from animal sources, usually more than 70%. They have specialized teeth and strong jaws to capture and efficiently process their prey. | Wolves, crocodiles, and great white sharks |
| Mesocarnivores | Mesocarnivores are carnivores that consume both animal and plant-based foods, with a more balanced diet. They generally have a broader range of prey items and can adapt to different food sources. | Raccoons, foxes, and skunks |
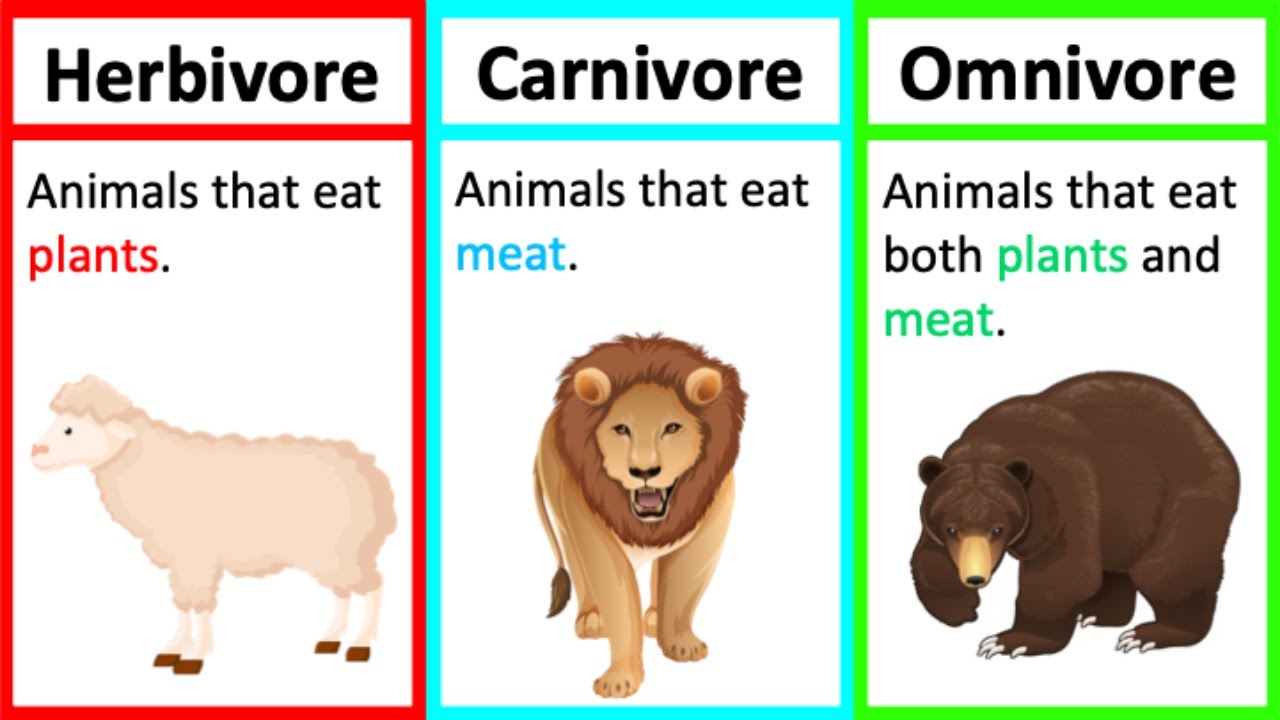
The Great Divide: Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores—Unveiling the Secrets of Animal Diets
What is Carnivore?
Carnivore is a term used to describe animals that primarily eat meat as their main source of nutrition. These animals have unique physiological and anatomical adaptations that allow them to efficiently hunt, capture, and consume other animals. Carnivores can be found in various ecosystems around the world and play essential roles in maintaining the balance of nature.
Types of Carnivores
There are several categories of carnivores, each with its own distinctive characteristics. The main types of carnivores include:
Obligate Carnivores
Obligate carnivores are animals that are exclusively dependent on a diet consisting solely of animal flesh. They lack the ability to digest plant matter effectively and rely on the nutrients found in meat for their survival. Examples of obligate carnivores include big cats such as lions, tigers, and cheetahs.
Facultative Carnivores
Facultative carnivores are more flexible in their dietary choices and can consume both animal and plant matter. While they have the capability to digest plant-based foods, they primarily rely on a diet rich in meat to meet their nutritional needs. Canids like wolves and foxes fall into this category.
Insectivores
Insectivores are a specialized group of carnivores that primarily feed on insects and other invertebrates. These animals have unique adaptations, such as specialized teeth and claws, to capture and consume their prey. Examples of insectivores include anteaters, armadillos, and certain species of bats.
Piscivores
Piscivores are carnivores that primarily consume fish. They are well adapted to aquatic environments and have specialized hunting techniques to catch their prey. Animals such as bears, otters, and certain species of birds, like the osprey, are considered piscivores.
Scavengers
Scavengers are carnivores that feed on dead and decaying animals. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem by helping to clean up and recycle nutrients from carcasses that would otherwise go to waste. Examples of scavengers include vultures, hyenas, and certain species of beetles.
Adaptations of Carnivores
Carnivores have evolved specific adaptations that allow them to efficiently hunt and consume their prey. These adaptations include:
Sharp Teeth and Claws
Carnivores possess sharp, pointed teeth that are well-suited for tearing flesh and crushing bones. These teeth enable them to efficiently capture and consume their prey. Additionally, many carnivores have retractable claws that can be extended when needed for hunting or climbing.
Enhanced Senses
Carnivores have highly developed sensory systems, including acute vision, hearing, and smell. These heightened senses allow them to detect prey from a distance, track their movements, and locate potential food sources. Carnivores often have forward-facing eyes to provide better depth perception for accurate hunting.
Speed and Agility
Many carnivores are exceptionally fast and agile, allowing them to chase down and capture their prey. Animals like cheetahs can reach incredible speeds of up to 70 miles per hour in short bursts, while others, like leopards, possess incredible climbing abilities that aid in ambushing their prey from treetops.
Powerful Jaws and Digestive Systems
Carnivores have strong jaws and digestive systems designed to handle the demands of consuming meat. Their jaws often have a powerful bite force that enables them to tear through tough hides and bones. Additionally, carnivores have shorter digestive tracts that facilitate the quick digestion of meat, as it requires less time to break down compared to plant matter.
Importance of Carnivores in Ecosystems
Carnivores play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems. Their presence helps regulate populations of prey species, preventing overpopulation, and ensuring the survival of diverse plant and animal communities. The absence or decline of carnivores can lead to ecological imbalances, such as increased competition between prey species and disruptions in food chains.
Carnivores also contribute to nutrient cycling within ecosystems. As scavengers, they help remove dead animals from the environment, preventing the spread of diseases and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. Their hunting activities can also influence the behavior and movements of prey species, leading to a more dynamic and resilient ecosystem.
Conservation Challenges
Carnivores face numerous conservation challenges due to habitat loss, poaching, and conflicts with human activities. As human populations expand and encroach upon natural habitats, carnivores often come into direct contact with humans and their livestock. This can lead to retaliatory killings, as carnivores may prey on livestock or pose a perceived threat to human safety.
Conservation efforts focus on protecting carnivores and their habitats, implementing measures to minimize human-wildlife conflicts, and raising awareness about the importance of these animals in maintaining healthy ecosystems. By understanding the ecological roles and unique adaptations of carnivores, we can work towards coexistence and ensure the long-term survival of these remarkable creatures.
Conclusion
Carnivores are fascinating creatures that have evolved specialized adaptations to thrive in their respective environments. From obligate carnivores to insectivores and scavengers, each type of carnivore plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of nature. Understanding the importance of carnivores and the challenges they face is crucial for their conservation and the preservation of diverse ecosystems worldwide.